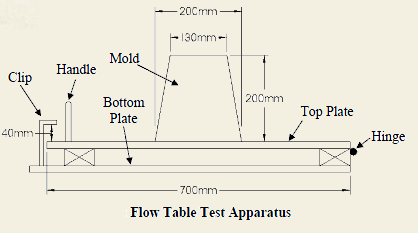
Pure water is neutral in nature with pH 7. Due to the presence of dissolved minerals in rain water, the pH increases and becomes alkaline. Alkalinity in water is due to the presence of hydroxide (OH), carbonate (CO3) and bicarbonate
Estimation of Alkalinity of Water by Titrating it against standard Sulphuric Acid solution – Chemical Practical