An operational amplifier (often op-amp or opamp) is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op-amp produces an output potential (relative to circuit ground) that is typically hundreds of thousands of times larger than the potential difference between its input terminals. Operational amplifiers had their origins in analog computers, where they were used to perform mathematical operations in many linear, non-linear and frequency-dependent circuits. The popularity of the op-amp as a building block in analog circuits is due to its versatility. Due to negative feedback, the characteristics of an op-amp circuit, its gain, input and output impedance, bandwidth etc. are determined by external components and have little dependence on temperature coefficients or manufacturing variations in the op-amp itself.
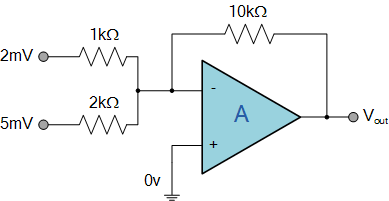
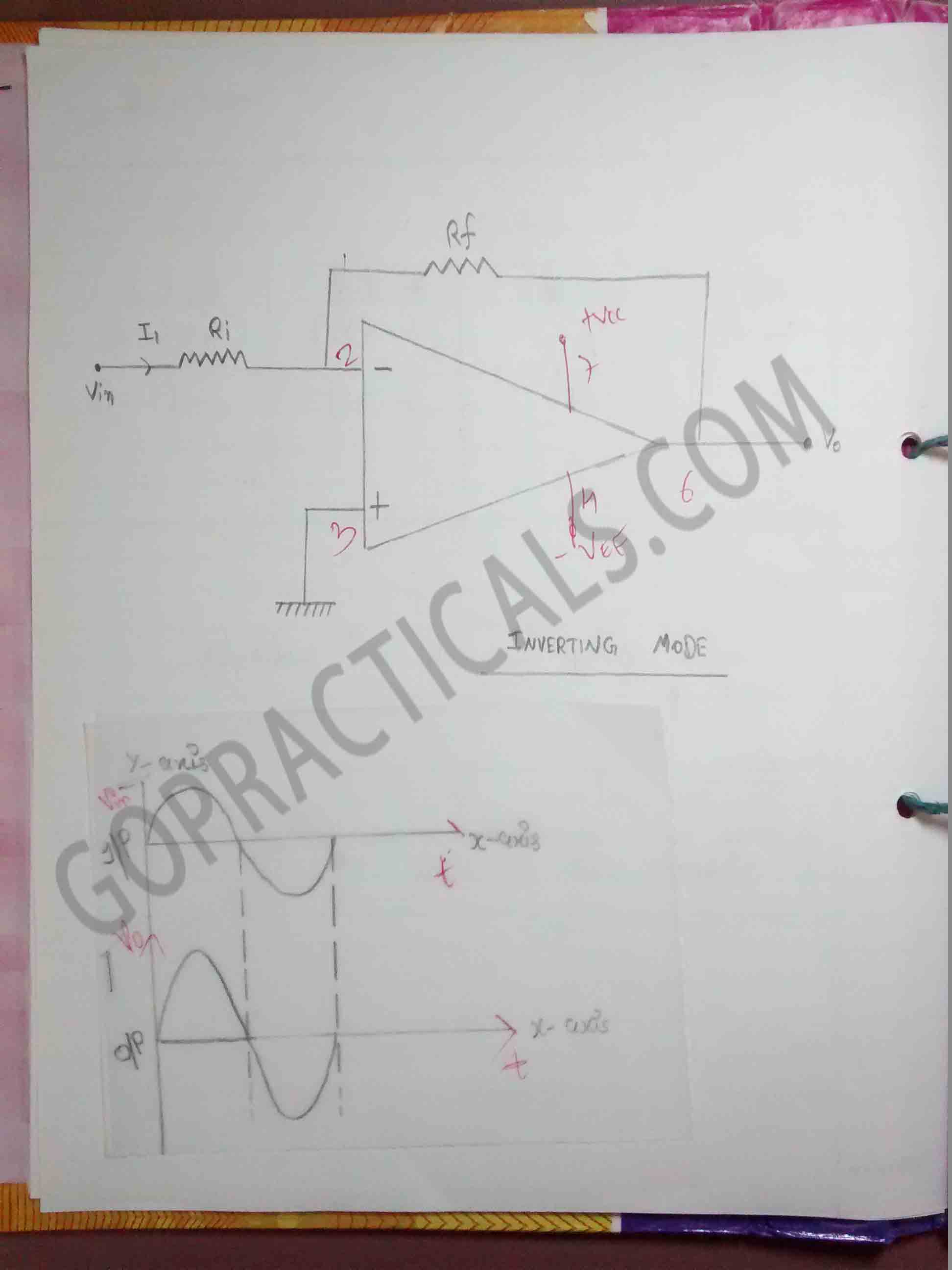
Fig: op-amp as adder circuit
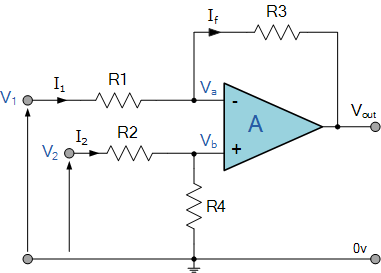
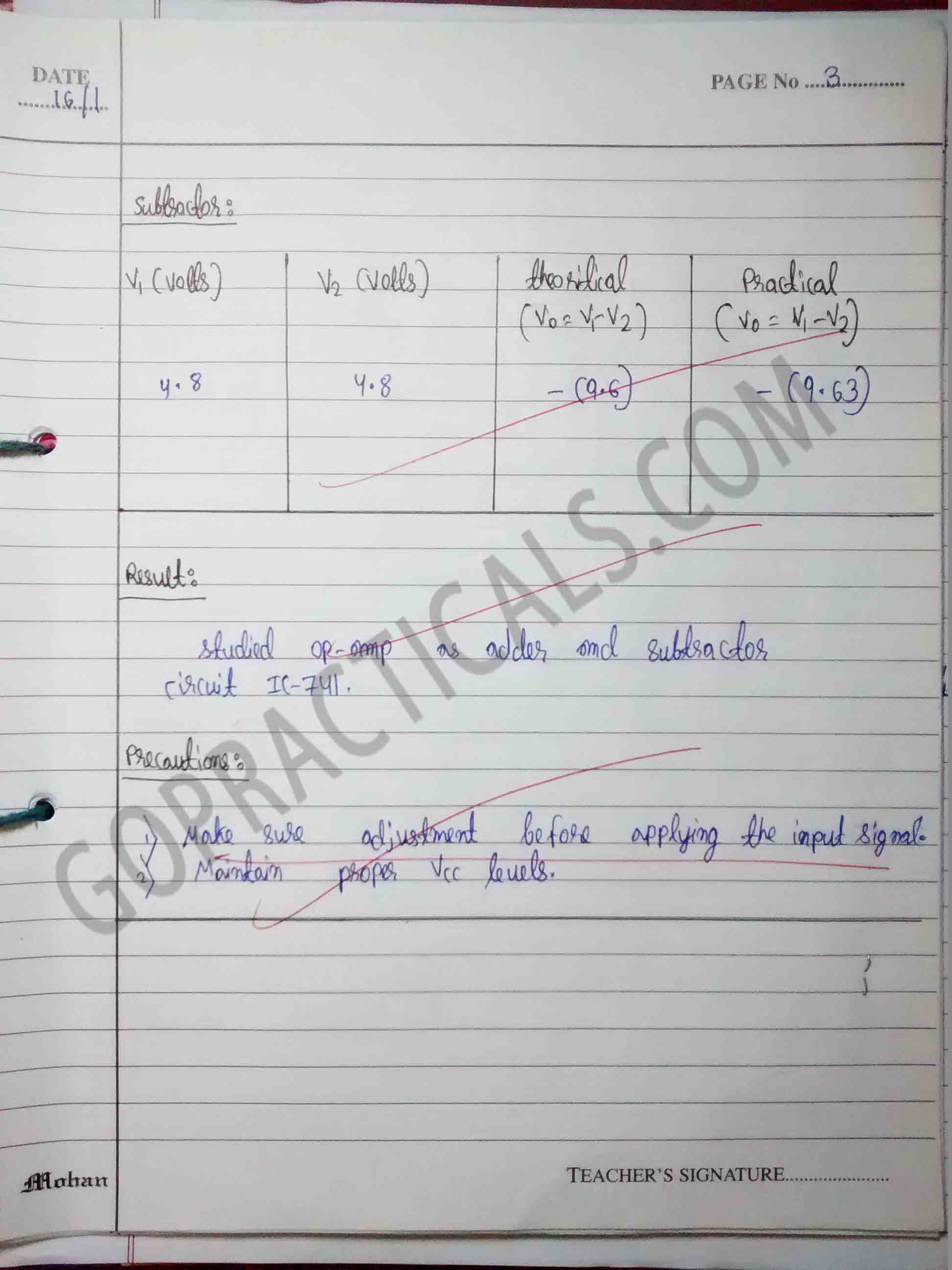
Fig: op-amp as subtractor circuit.
Practical to study working of op-amp as adder and subtractor circuit

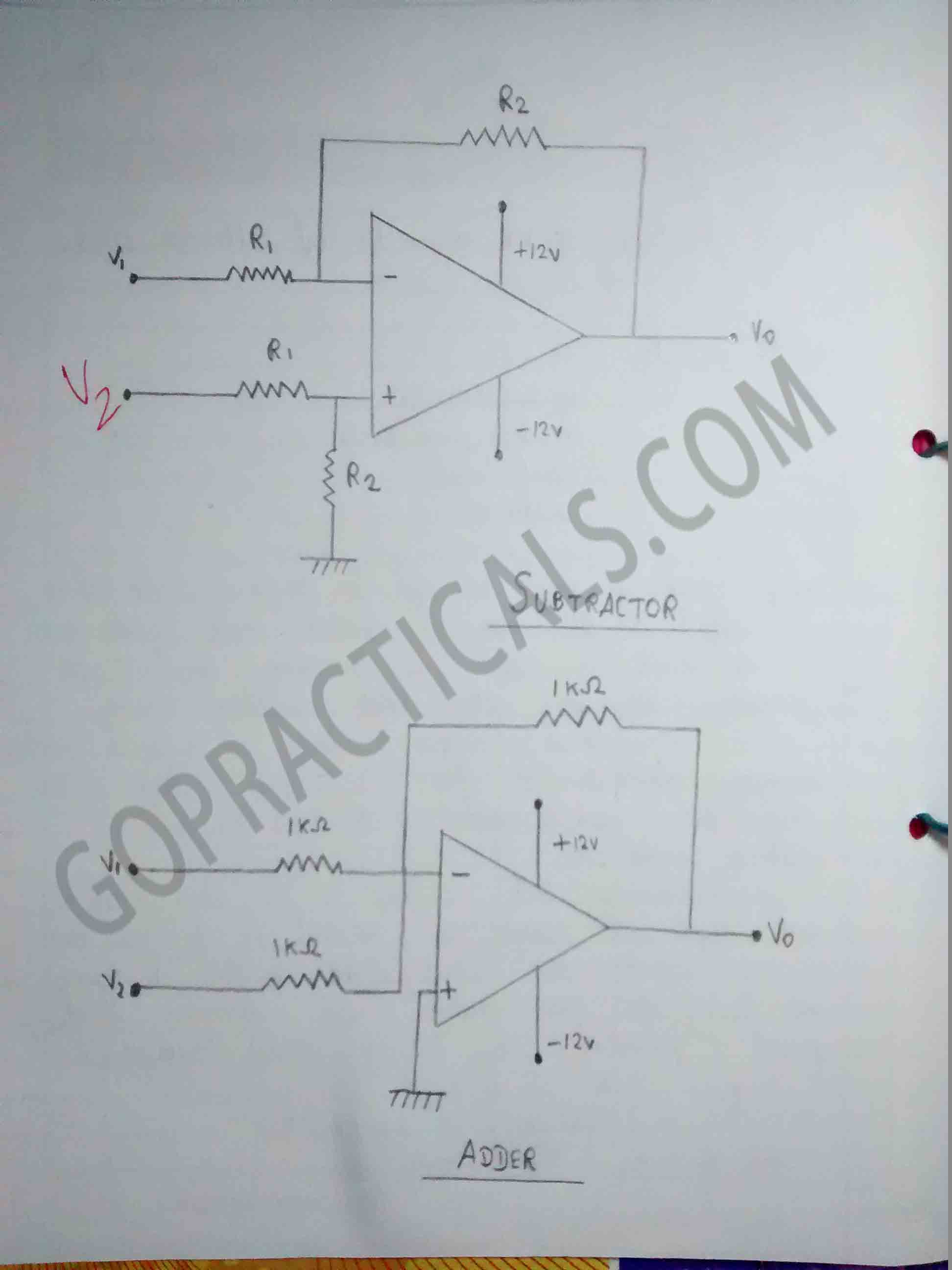
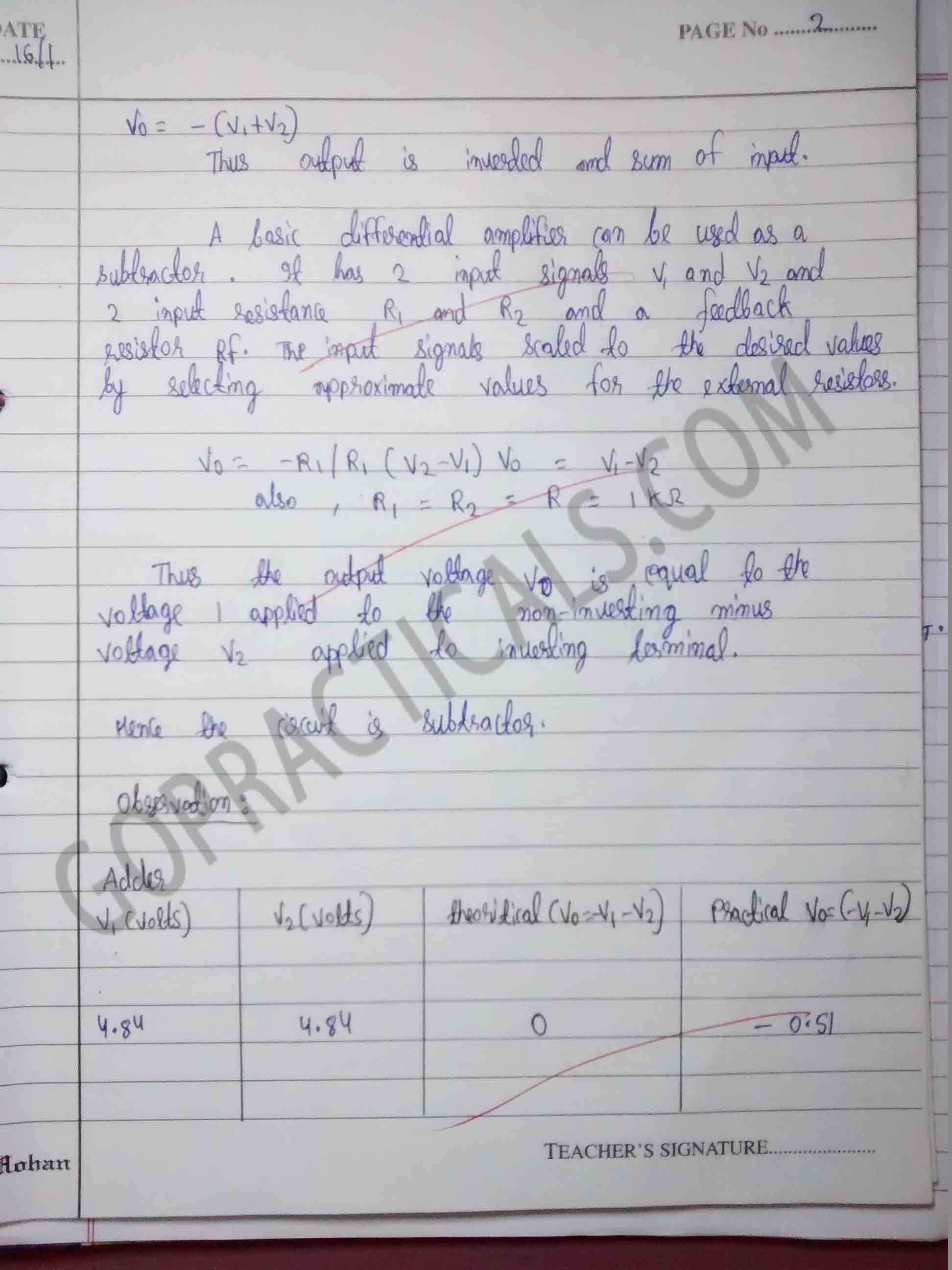
Watch this Video to know more about op-amp as adder and subtractor circuit
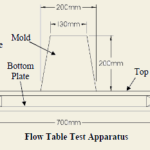
Also Check Out – Consistency of Concrete by Slump Cone
Thanks for visiting us…

Very good post, keep up the good work. If you have time maybe you can check mine, Thanks!