In its simplest form, concrete is a mixture of paste and aggregates, or rocks. The paste, composed of portland cement and water, coats the surface of the fine (small) and coarse (larger) aggregates. Through a chemical reaction called hydration, the
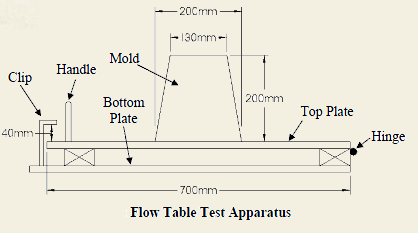
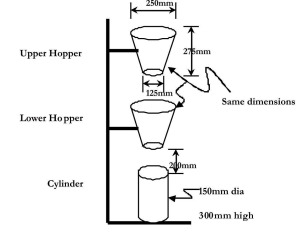
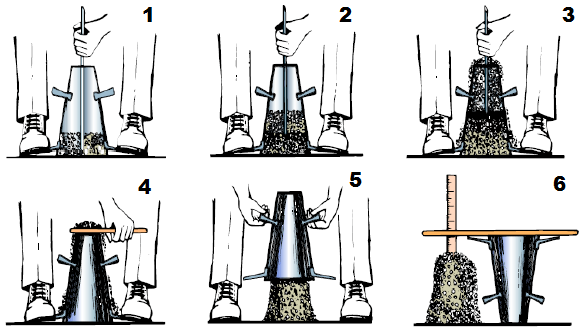
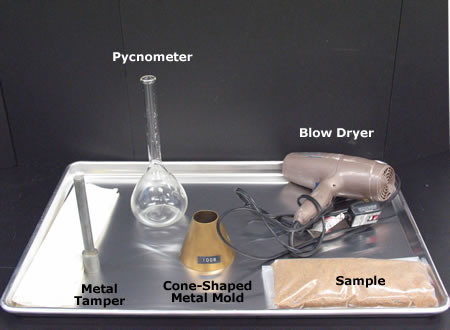
To measure the flow and work ability of concrete by using Flow Table – Concrete Practical